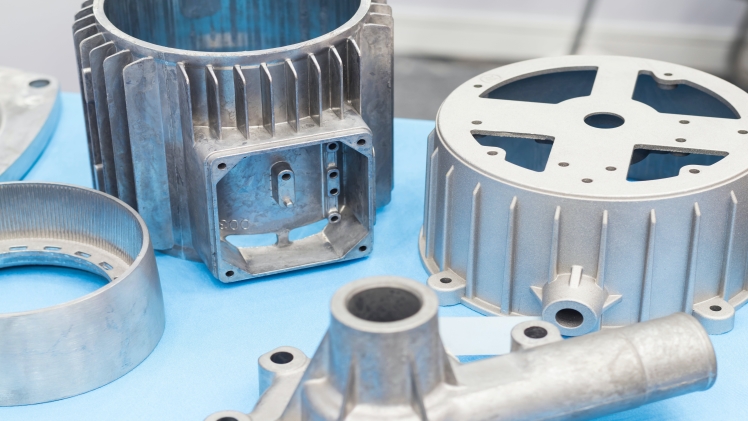
What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a metal casting process that involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. The mold, also known as a die, is usually made of two parts, and the shape of the final product is determined by the design of the mold.
The die-casting process was first developed in the early 1800s and has become one of the most popular methods for producing high-quality, complex metal parts. It offers many advantages over other manufacturing processes, such as precision, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. Die casting is widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods.
The basic steps involved in die casting are preparing the mold, injecting molten metal under high pressure into the mold cavity, cooling and solidifying the metal inside the mold to form the desired shape, ejecting the part from the die after it has cooled down, and trimming any excess material. Depending on the alloy type, this process can be done using hot or cold chamber machines.
Benefits of die-casting;
Die casting is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten metal into a mold to create complex and intricate shapes. This versatile technique has been around for decades and is the preferred choice for producing high-quality metal parts and products. One of the main reasons for its popularity is its numerous benefits, making it an ideal choice for various industries.
In this section, we will explore some of the critical benefits of die casting that make it a top choice among manufacturers.
1. High Precision and Accuracy:
Die casting allows for high precision and accuracy in complex shapes with tight tolerances. The molds used in this process are designed with great attention to detail, ensuring that each part produced is consistent in size, shape, and dimensions. This level of precision and accuracy cannot be achieved with other manufacturing methods, such as forging or machining.
2. Cost-Effective:
Another significant advantage of die casting is its cost-effectiveness. Compared to other production methods, such as sand casting or investment casting, die casting requires less labor and time to produce large quantities of parts. This makes it a more economical option for mass production, resulting in lower per-unit costs.
3. Versatility:
Die casting offers versatility in materials, giving manufacturers the flexibility to choose from a wide range of alloys based on their specific requirements. Numerous options can cater to different product needs, from aluminum and zinc to copper and brass.
Types of Common Materials Used in Die Casting;
Die casting is a popular manufacturing method for creating high-quality, complex metal components with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. It involves injecting molten metal into a steel mold under high pressure, allowing the metal to solidify and take on the shape of the mold. This process is highly versatile and can produce various products for automotive, aerospace, electronics, and other industries.
Selecting the suitable material for your product is crucial in die casting. The material choice will significantly impact the mechanical properties, surface finish, and overall quality of your finished product. There are several types of materials commonly used in die casting; let’s take a closer look at each one:
1. Aluminum Alloys:
Aluminum is the most widely used material in die casting due to its lightweight yet strong properties. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for various applications, from consumer electronics to automotive parts. Some common aluminum alloys used in die casting include A380, A383, A360, and ADC12.
2. Zinc Alloys:
Zinc alloys have gained popularity recently due to their low melting point and easy flow characteristics. They offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and are often used to produce small precision components such as gears and electrical connectors.
3. Magnesium Alloys:
Magnesium alloys are known for their lightweight properties (about 33% lighter than aluminum) yet maintain a high strength-to-weight ratio. Magnesium alloys are another popular choice for die casting, thanks to their lightweight and robust properties. These alloys have a high strength-to-weight percentage, making them ideal for applications where weight is crucial.
Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Product;
Choosing the suitable alloy for your product is crucial in the die-casting process. The type of alloy used will significantly impact your final product’s quality, properties, and performance. With so many different alloys available, it can be overwhelming to determine which one is best suited for your specific needs. This section will discuss some important factors when choosing a suitable alloy for your product.
- Design Requirements: Before selecting an alloy, it is essential to understand the design requirements of your product. This includes strength, hardness, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. Different alloys have varying levels of these properties, and choosing one that meets your product’s specific demands is essential.
- Material Compatibility: Another critical factor to consider is the compatibility between the chosen alloy and other materials that may come into contact with your product. For example, if your product requires welding or painting post-casting, you must ensure that the chosen alloy is compatible with these processes.
- Cost: The cost of material also plays a significant role in choosing the right alloy for your product. While some high-performance alloys offer superior properties, others may be more expensive. It is essential to balance cost and performance to ensure you get value for money without compromising quality.
Cost Comparison of Different Materials;
When choosing the suitable material for your die-casting products, cost is one of the most important factors. Different materials have varying prices, and it’s essential to understand how they compare to make an informed decision.
- Aluminum alloys are often considered the most cost-effective option for die casting. This is due to their abundant availability and relatively low production costs. In addition, aluminum has a lower melting point than other materials, making it easier and cheaper to handle during the casting process. This results in lower energy consumption and tooling costs.
- On the other hand, copper alloys tend to have higher material costs compared to aluminum. However, they offer superior strength and corrosion resistance, which can benefit specific applications. Copper alloys are also known for their excellent thermal conductivity, making them suitable for high-temperature environments.
- Zinc alloys fall somewhere in between aluminum and copper in terms of cost. They have a slightly higher material cost than aluminum but are still more affordable than copper. Zinc is also known for its exceptional fluidity, allowing for intricate designs and thin walls in castings without compromising structural integrity.
- Magnesium alloys may have a higher initial cost compared to other materials, but they offer significant savings in the long run due to their lightweight properties. Magnesium is about 33% lighter than aluminum and 75% lighter than steel, making it an ideal choice for industries where weight reduction is crucial such as automotive or aerospace.
Conclusion;
In conclusion, choosing the alloy for your die-casting products is crucial in ensuring their quality and functionality. By understanding the common materials used in die casting and their properties, you can make an informed decision that will meet your specific product needs. Whether aluminum, zinc, magnesium, or copper-based alloys, each has unique advantages and applications. So take the time to consider all options before making a choice and consult with experts if needed. With the proper alloy selection, you can create high-quality products to satisfy you and your customers.